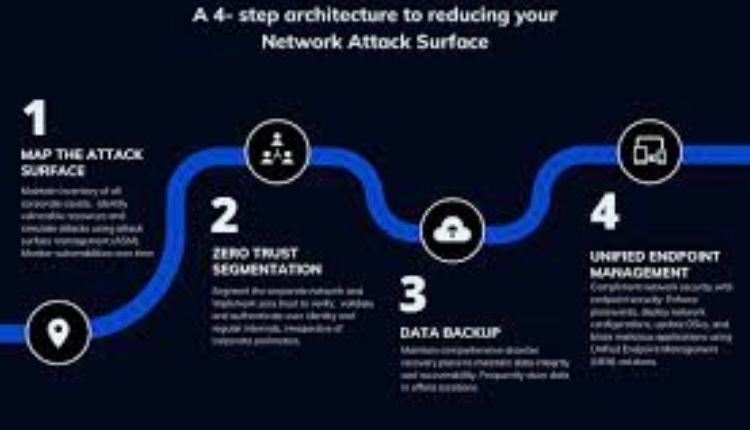
Nowadays, the security of networks and data is paramount. With cyber threats becoming more sophisticated, traditional security models that rely on perimeter defences are no longer sufficient. Zero Trust and network segmentation come into play, offering a robust framework to protect sensitive information and minimise attack surfaces. Let’s look into the benefits these strategies bring to modern enterprises.
Protecting a Distributed Workforce
One of the most significant advantages of adopting a zero trust security architecture is its ability to secure distributed and remote workforces. Since employees nowadays work from various locations—home offices, co-working spaces, and even public Wi-Fi networks—security risks are amplified. Traditional security models often fall short in this scenario, assuming anyone within the network perimeter is trustworthy.
However, Zero Trust turns this assumption on its head by requiring every user, whether inside or outside the network, to be verified before access is granted. This approach is particularly beneficial for organisations with a large remote workforce. By verifying the identity and context of each user, Zero Trust provides a level of security that adapts to the modern work environment.
Simplified Access Management
Managing access across a sprawling enterprise network can be challenging, but Zero Trust simplifies this process through the implementation of Single Sign-On (SSO) and multi-factor authentication (MFA). SSO allows employees to access multiple applications with a single set of credentials, reducing the friction of constant logins and improving productivity. When combined with MFA, this system becomes even more secure, as it requires additional verification steps beyond just a password.
This streamlined access management enhances security and makes it easier for IT teams to manage user permissions. By centralising control, Zero Trust reduces the chances of unauthorised access and ensures that users only have the privileges necessary to perform their duties.
Enhanced Visibility and Monitoring
Another critical benefit is the comprehensive visibility and monitoring it offers. Traditional security models often struggle to clearly understand all network activities. In contrast, Zero Trust is built on the principle of continuous monitoring and validation, which means that every interaction within the network is logged and verified.
This level of scrutiny enables organisations to detect anomalies and potential threats more effectively. For instance, if a user’s behaviour deviates from the norm, the system can flag this activity for further investigation. Zero Trust provides a unified network view by consolidating data from various sources. It allows for quicker and more accurate threat detection.
Layered Security for Comprehensive Protection
Zero Trust’s approach to security is inherently layered, offering multiple defences against various types of threats. Here’s how:
- One of the critical components of this is network segmentation, which involves dividing the network into smaller, isolated segments.
- This segmentation ensures that even if a cybercriminal gains access to one part of the network, they cannot quickly move laterally to other parts.
- This containment strategy significantly reduces the potential damage that a breach can cause. For example, in a segmented network, sensitive data, such as financial records or customer information, can be isolated from less critical areas, making it harder for attackers to reach high-value targets.
- By combining micro-segmentation, organisations create a formidable barrier against internal and external threats.
Regulatory Compliance and Auditing
Maintaining compliance is a top priority for many organisations in an era of stringent data protection regulations. Zero Trust architecture supports this goal by implementing strict access controls and maintaining detailed network activity logs. These logs provide a comprehensive audit trail, making it easier for organisations to demonstrate compliance with regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and others.
Moreover, network segmentation ensures that sensitive data is kept separate and secure, further aiding in compliance efforts. It helps avoid costly fines and builds trust with customers and stakeholders by committing to safeguarding their data.
Zero trust security and network segmentation offer a powerful combination of essential benefits for modern cybersecurity. By adopting it, organisations can reduce their attack surface and build a resilient security framework that can adapt to evolving threats. Since cyber threats are ever-present, these strategies are no longer just an option—they are necessary for any organisation looking to safeguard its digital assets.